Tandem Wing Tail-Sitter
This project started with an innovative drone competition held by the Taipei Computer Associate. The primary objective of this competition was to design a drone capable of carrying a 2 kg payload and completing a 15 km flight. In order to achieve this goal, we devised a tail-sitter with the tandem wing configuration. The design allows for vertical take-off and landing while maintaining energy efficiency by flying as a fixed-wing plane, utilizing the high lift-drag ratio inherent in the tandem wing configuration.
To validate this proposal, we performed a fluid simulation conducted via ANSYS to gather the aerodynamic data of the drone under various wind conditions. Moreover, a PID-based control scheme was also proposed to stabilize the drone while vertically taking off with the side wind. The control scheme enables the drone to withstand side winds up to a maximum velocity of 5 m/s. The effectiveness of the PID controller was verified using SIMULINK.
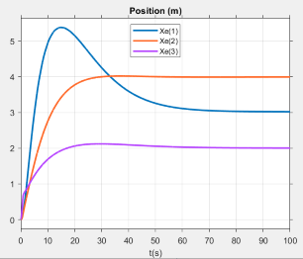
The position of the drone converges to the given set point under a 5m/s side wind.
